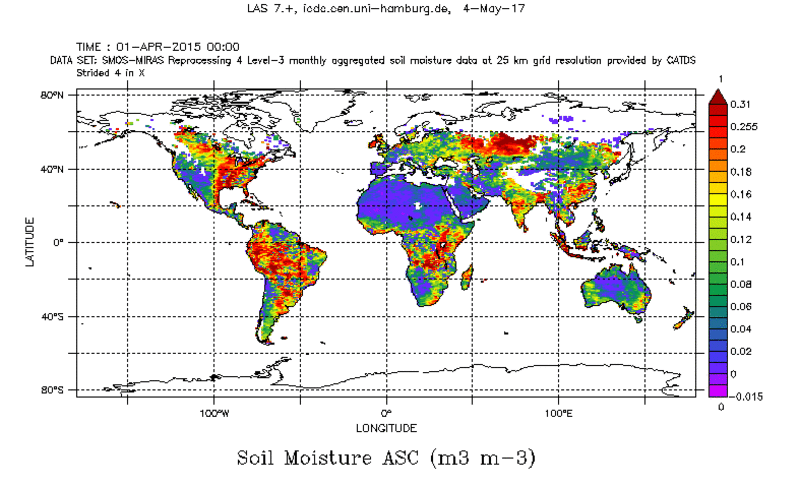
Soil Moisture from SMOS data
Topics
- Access
- Description
- Parameters
- Coverage, spatial and temporal resolution
- Data quality
- Contact person
- References
- Data citation
Access
RESTRICTED: This link to the data set is only available for a restricted user group. The data set is only accessible in CEN/MPI net or accessible from external nets with a customer account. Please contact ICDC if you would like to access this data from outside the network.
- View soil moisture data at LAS
- Access soil moisture data via OPeNDAP
- Data access via file system: /data/icdc/land/smos_soilmoisture
Description
Brightness temperature measurements in L-Band (1.0 - 2.0 GHz) acquired by the MIRAS sensor aboard the Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) sensor are used to retrieve a global data set of the near surface (0 - 5 cm) soil moisture.
For the soil moisture retrieval an iterative minimization of a cost function is carried out. That cost function is constructed from the quadratic differences of observed and modeled brightness temperatures and from the quadratic differences of retrieved and a-priori geophysical parameters such as the soil moisture, the soil dielectric constant and the vegetation optical depth - all scaled with their uncertainty.
This Level-3 product retrieval uses multi-angular, multi-orbit brightness temperature measurements of the same location collected for the day of soil moisture retrieval and from days up to three days in the past and three days ahead of the respective day, i.e. a 7-day period. More details about the soil moisture retrieval is given in the ATBD and in the paper by Al Bitar et al. (see references).
We note that this Level-3 product does not follow the common procedure and is not retrieved from the level-2 soil moisture products but for ease of usage is retrieved directly from the Level 1B data.
We offer re-processed data (RE04, until including May 5, 2015) and operational data (OPER, since including May 6, 2015).
Last update of data set at ICDC: May 8, 2025.
Parameters
| Name | Unit / Range | Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| soil moisture | m³/m³ | daily, monthly |
| soil moisture retrieval uncertainty | m³/m³ | daily, monthly |
| number of valid soil moisture values per grid cell | 0 ... 31 | monthly |
| initial number of SMOS measurements per grid cell | - | daily |
| useful number of SMOS measurements per grid cell | - | daily |
| soil fraction appropriate for retrieval per grid cell | 0 ... 100 % | daily, monthly |
| forest fraction per grid cell | 0 ... 100 % | daily, monthly |
| nadir vegetation optical depth | Neper | daily*, monthly |
| uncertainty of nadir vegetation optical depth | Neper | daily*, monthly |
| nadir forest optical depth | Neper | monthly |
| uncertainty of nadir forest optical depth | Neper | monthly |
| skin temperature | K | daily |
| top (0-7cm) soil layer temperature | K | daily |
| SMOS data acquisition time per grid cell | s | daily |
| permanent surface category | - | daily |
Coverage, spatial and temporal resolution
Period and temporal resolution:
- Daily: 2010-01-15 to 2015-05-05 (RE04), 2015-05-06 to 2025-03-31 (OPER)
- Monthly: 2010-01 to 2015-04 (RE04), 2015-05 to 2025-03 (OPER)
- Missing data: 2021-04-01 until 2021-05-24
Coverage and spatial resolution:
- Global
- Spatial resolution: about 25 km x 25 km, EASE version 2, cylindrical grid (= equidistant longitudes but non-equidistant latitudes)
- Geographic longitude: 179.8703°W to 179.8703°E
- Geographic latitude: 83.51714°S to 83.51714°N
- Dimension: 584 rows x 1388 columns
- Altitude: following terrain
Format:
- NetCDF
Data quality
This data set contains uncertainty estimates for the soil moisture product. These estimates are based on the various input parameters and assumptions.
Vegetation canopy and soil temperature have a considerable influence on the retrieval quality. Therefore does the data product contain the fractional coverage of forest and non-forest surfaces for each grid cell. In addition to that, both products contain an estimate of the canopys' optical depth. The higher that value is, the more likely the soil moisture value might be biased. The optical depth dos also come with an uncertainty estimate.
The daily data contain in addition the soil (surface) temperature from ECMWF land surface model data.
In order to better understand why in which regions no soil moisture is retrieved a surface type map is provided along with the daily data.
We did not include a number of additional data sets which were included in the original daily data set. These are the brightness temperature at the surface and at the top of the atmosphere, the retrieved soil dielectric constant, and a bit-encoded very detailed quality flag (see Product Description in the references).
We note that data from the ascending overpasses (denote by "__A__" in the filename) are potentially less influenced by ionospheric effects and by diurnal temperature variations / gradients.
For more information about evaluation / validation activities and the difficulty to evaluate satellite soil moisture products we refer to the references.
Contact
Centre Aval de Traitement des Donnees SMOS (CATDS)
Centre d'Etudes Spatiales de la Biosphere (CESBIO)
Universite de Toulouse, Toulouse, France
email: support (at) catds.frAhmad Al Bitar
Centre d'Etudes Spatiales de la Biosphere (CESBIO)
Universite de Toulouse, Toulouse, France
email: ahmad.albitar (at) cesbio.cnes.frStefan Kern
University of Hamburg
email: stefan.kern (at) uni-hamburg.de
References
Literature:
- Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD)
- Data Product Description
- Al Bitar, A., et al., 2017, The global SMOS level 3 daily soil moisture and brightness temperature maps, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 9, 293-315, https://doi.org/10.5195/essd-9-293-2017
- Al-Yaari, A., et al., 2014, Global-scale comparison of passive (SMOS) and active (ASCAT) satellite based microwave soil moisture retrievals with soil moisture simulations (MERRA-Land), Rem. Sens. Environ., 152, 614-626, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.07.013
- Al-Yaari, A., et al., 2017, Evaluating soil moisture retrievals from ESA's SMOS and NASA's SMAP brightness temperature datasets, Rem. Sens. Environ., 193, 257-273, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.03.010
- Louvet, S., et al., 2015, SMOS soil moisture product evaluation over West-Africa from local to regional scale, Rem. Sens. Environ., 156, 383-394, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.10.005
- van der Schalie, R., et al., 2015, SMOS soil moisture retrievals using the land parameter retrieval model: Evaluation over the Murrumbidgee Catchment, Southeast Australia, Rem. Sens. Environ., 163, 70-79, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.03.006
- Holgate, C. M., et al., 2016, Comparison of remotely sensed and modelled soil moisture data sets across Australia. Rem. Sens. Environ., 186, 479-500.
- Jing, W., et al., 2018, A comparison of ECV and SMOS soil moisture products based on OzNet monitoring network, Remote Sensing, 10(5), 703, doi:10.3390/rs10050703, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050703.
Data citation
Please cite the data as follows:
CATDS/CESBIO ESA-SMOS soil moisture of reprocessing RE04 and operational data (OPER) distributed via ftp://ifremer.fr as daily / monthly [choose which apply] global maps [last access: April 14, 2025] were obtained from: Integrated Climate Data Centre (ICDC), CEN, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany.
and
Al Bitar, A., A. Mialon, Y. H. Kerr, F. Cabot, P. Richaume, E. Jacquette, A. Quesney, A. Mahmoodi, S. Tarot, M. Parrens, A. Al-Yaari, T. Pellarin, N. Rodriguez-Fernandez, and J.-P. Wigneron, 2017, The global SMOS level 3 daily soil moisture and brightness temperature maps, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 9, 293-315, https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-293-2017.
and with the following acknowledgments:
Thanks to ICDC, CEN, University of Hamburg for data support.
