Vegetation Index NDVI from MODIS
Topics
- Access
- Description
- Parameters
- Coverage, spatial and temporal resolution
- Data quality
- Contact person
- References
- Data citation
Access
UNRESTRICTED:
- Get AQUA data via HTTP (wget shell script for all AQUA files)
- Get TERRA data via HTTP (wget shell script for all TERRA files)
- Access TERRA und AQUA data via OPeNDAP
RESTRICTED: This link to the data set is only available for a restricted user group. The data set is only accessible in CEN/MPI net or accessible from external nets with a customer account. Please contact ICDC if you would like to access this data from outside the network.
- View vegetationindex data at LAS: AQUA | TERRA
- MODIS TERRA Data access via file system: /data/icdc/land/modis_terra_vegetationindex
- MODIS AQUA Data access via file system: /data/icdc/land/modis_aqua_vegetationindex
Description
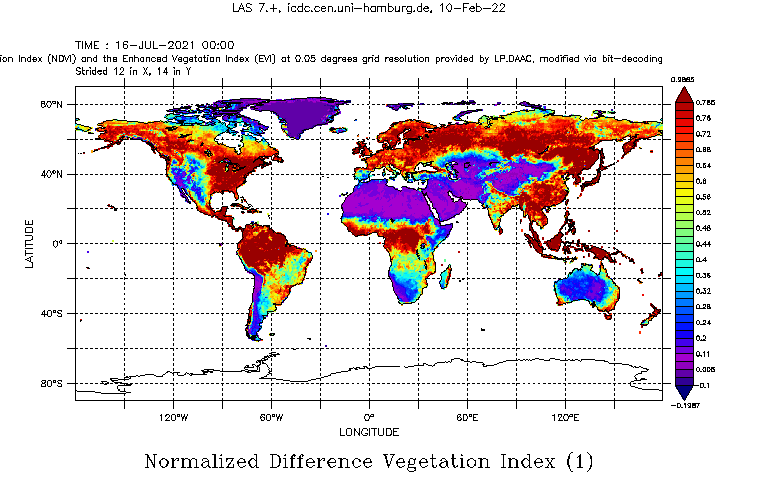
This data set comprises the Normalized Differential Vegetation Index (NDVI) and the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) together with uncertainty estimates, various quality flags, solar zenith angles, number of 1 km grid cells used, and reflectances / radiances of the 4 MODIS channels used for the retrieval.
Both indices are based on the difference: reflectance observed in the near-infrared (NIR) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum minus reflectance observed in the red portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Areas with photosynthetically active vegetation absorb much more radiation in the red portion of the electromagnetic spectrum than areas without any or with photosynthetically inactive vegetation. This is due to the pigments in the leaves, needles, etc. In contrast, absorption of NIR radiation is low for both surface types. However, the amount of NIR radiation transmitted and/or scattered is a function of the surface type / roughness. Therefore, the difference of the reflectances is small for areas without any or with photosynthetically inactive vegetation and high for areas with photosynthetically active vegetation. Note that in areas with a lot of vegetation the dependence of the NIR-radiation scattering and/or transmission on the surface type / roughness helps to overcome saturation effects in the red portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and therefore allows a better separation of high NDVI values.
The impact of clouds, aerosols, sensor noise (and other error sources not mentioned here explicitly) is mitigated using radiative transfer modeling on the one hand. On the other hand these impacts are mitigated by normalizing the above-mentioned difference with the sum of the used reflectances (NDVI) or with these reflectances, the reflectance in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and additional factors (EVI). For more details we recommend to look into the User's Guide (see references).
The data set (MODIS collection 6.1) offered here (MOD13C2 and MYD13C2) has monthly temporal resolution and allows to monitor the seasonal cycle of vegetation development.
Last update of data set at ICDC: November 21, 2024.
Parameters
| Name | Unit |
|---|---|
| NDVI | - |
| NDVI standard deviation | - |
| EVI | - |
| EVI standard deviation | - |
| quality flag (general) | - |
| quality flag (detailed) | - |
| number of useful 1 km grid cells | - |
| quality flag aerosol model | - |
| sun zenith angle | degree |
| reflectance red channel (620-670 nm, channel 1) | - |
| reflectance blue channel (459-479 nm, channel 3) | - |
| reflectance NIR (841-876 nm, channel 2) | - |
| radiance middle IR (2105-2155 nm, channel 7) | - |
Coverage, spatial and temporal resolution
Period and temporal resolution:
- 2000/02 - 2024/09 (TERRA); 2002/07 - 2024/09 (AQUA)
- Monthly
Coverage and spatial resolution:
- Global
- Spatial resolution: 0.05° x 0.05° (about 5600 m, Climate Modeling Grid)
- Geographical longitude: 179.975°W to 179.975°E
- Geographical latitude: 89.975°S to 89.975°N
- Dimension: 3600 rows x 7200 columns
- Altitude: follows topography
Format:
- NetCDF
Data quality
This data set is based on re-calibrated MODIS observations of collection 061. Long-term inconsistencies caused by problematic calibration of particularly MODIS TERRA have been solved (Lyapustin et al., 2014, see references). Both, NDVI and EVI have been validated in a number of field campaigns and validation studies. The data set with monthly temporal resolution offered here is based on 16-day composites of MODIS NDVI and EVI at 1 km grid resolution. Radiative transfer modeling and a number of filters were used to mitigate or eliminate cloud and aerosol effects. The innovative elements in collection 061 are
- usage of Collection 6 vegetation cover and other auxiliary land surface data based on MODIS;
- usage of the Collection 6.1 cloud mask; pre-compositing of 250 m / 500 m reflectances / radiances prior to 8-day data sets instead of first deriving the NDVI/EVI and then performing the compositing.
The data set offered here contains 4 different quality flags; one gives general information about whether the quality is good or acceptable, in the latter case the recommendation is to look into the detailed quality flags, whether due to snow/ice or due to clouds a retrieval was not possible, or whether data are missing or NDVI/EVI have not been processed due to other reasons or have been filled with values from climatology.
The second quality flag gives a linearly scaled quality information:
- low value = low quality,
- high value = high quality.
The two remaining flag give information about the aerosol load and/or the aerosol model used to correct the observed radiances and the second one details how many useful NDVI or EVI values of the 1 km grid resolution product contribute to CMG-grid data set given here.
Contact
LP DAAC User Services
U.S. Geological Survey (USGS)
Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS)
email: LPDAAC (at) eos.nasa.govKamel Didan
Vegetation Index and Phenology Lab
University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, U.S.
email: didan (at) email.arizona.eduStefan Kern
University of Hamburg
email: stefan.kern (at) uni-hamburg.de
References
Literature:
- MODIS Vegetation Index User’s Guide (MOD13 Series) Version 3.10, September 2019 (Collection 6.1) (pdf, not barrier free)
- MODIS VEGETATION INDEX (MOD 13) ALGORITHM THEORETICAL BASIS DOCUMENT Version 3.1 (pdf, not barrier free)
- Lyapustin, A., Wang, Y., Xiong, X., Meister, G., Platnick, S., Levy, R., Franz, B., Korkin, S., Hilker, T., Tucker, J., Hall, F., Sellers, P., Wu, A., and Angal, A.: Scientific impact of MODIS C5 calibration degradation and C6+ improvements, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 7, 4353–4365, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-7-4353-2014, 2014.
- Huete, A., et al., 2002, Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation index. Rem. Sens. Environ., 83, 195-213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00096-2
- Huete, A., et al., 2011, MODIS Vegetation Indices, in: Land Remote Sensing and Global Environmental Change, edited by: Ramachandran, B., C. Justice, and M. J. Abrams, Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing, Springer, New York.
- Zhang, X., et al., 2017, Comparisons of global land surface seasonality and phenology derived from AVHRR, MODIS, and VIIRS data, J. Geophys. Res. - Biogeosci., 122, 1506-1525. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JG003811
- Zhang, Y., et al., 2017, Reanalysis of global terrestrial vegetation trends from MODIS products: Browning or greening? Rem. Sens. Environ., 191, 145-155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.018
Websites:
- The Vegetation Index and Phenology Research Group: Vegetation Index & Phenology Lab, http://vip.arizona.edu
- LP DAAC Website, https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/
- Data set Website: MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices Monthly L3 Global 0.05 Deg CMG, https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MOD13C2.061
Data citation, License, and Acknowledgement
Please cite the data as follows:
Note: When using MODIS AQUA instead of TERRA data, please replace "MOD" by "MYD".
K. Didan, (2021), MOD13C2 MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices Monthly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG V061. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC. https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MOD13C2.061; obtained from the Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC), located at the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center (lpdaac.usgs.gov) [last access: October 28, 2024], modified and converted into netCDF file format at the Integrated Climate Data Center (ICDC), CEN, University of Hamburg, Germany.
License: The data was published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY-4.0).
