Carbon removal from atmosphere unavoidable for 1.5 degree target
24 May 2018, by Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change

Photo: Sushobhan Badhai on Unsplash
How to remove carbon from the atmosphere? Comprehensive new studies with the contribution of CEN scientist Prof Jens Hartmann and Dr Thorben Amann show the potentials and risks of different negative emissions technologies.
Limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees will make the world increasingly dependent on technologies that extract CO2 from the atmosphere. However, technology development and expansion, as well as the start of pilot projects, are considerably lagging behind deployment in climate mitigation scenarios. In order to remain below the two-degree mark, however, the extensive use of a broad portfolio of "negative emission technologies" (NETs), as these techniques for CO2 removal are called, can be reduced to a minimum. This is one result of several new studies by the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC). The scientists led an international consortium that has now published the results in a special section of the journal Environmental Research Letters.
With these three comprehensive studies, the researchers point to a major gap in the dialogue between science and policy: With the Paris Agreement, the international community committed itself to limiting global warming to “well below two degrees Celsius.” However, the necessary deployment of NETs is currently hardly discussed in policy debates, although some of these technologies involve considerable conflicts for land use, water consumption or energy requirements among others. Negative emissions will likely be featured prominently in the Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) on the 1.5°C target, which will be published in autumn.
"Although policymakers like to set ever more ambitious targets in the climate negotiations, the concrete actions so far are lagging far behind. The result is a growing dependence on negative emissions," says Jan Minx, head of the MCC working group Applied Sustainability Science. "There is an urgent need for the international community not to further increase but reduce its dependence on technologies for carbon removal from the atmosphere. To achieve this, we need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions much more rapidly – also in Germany".
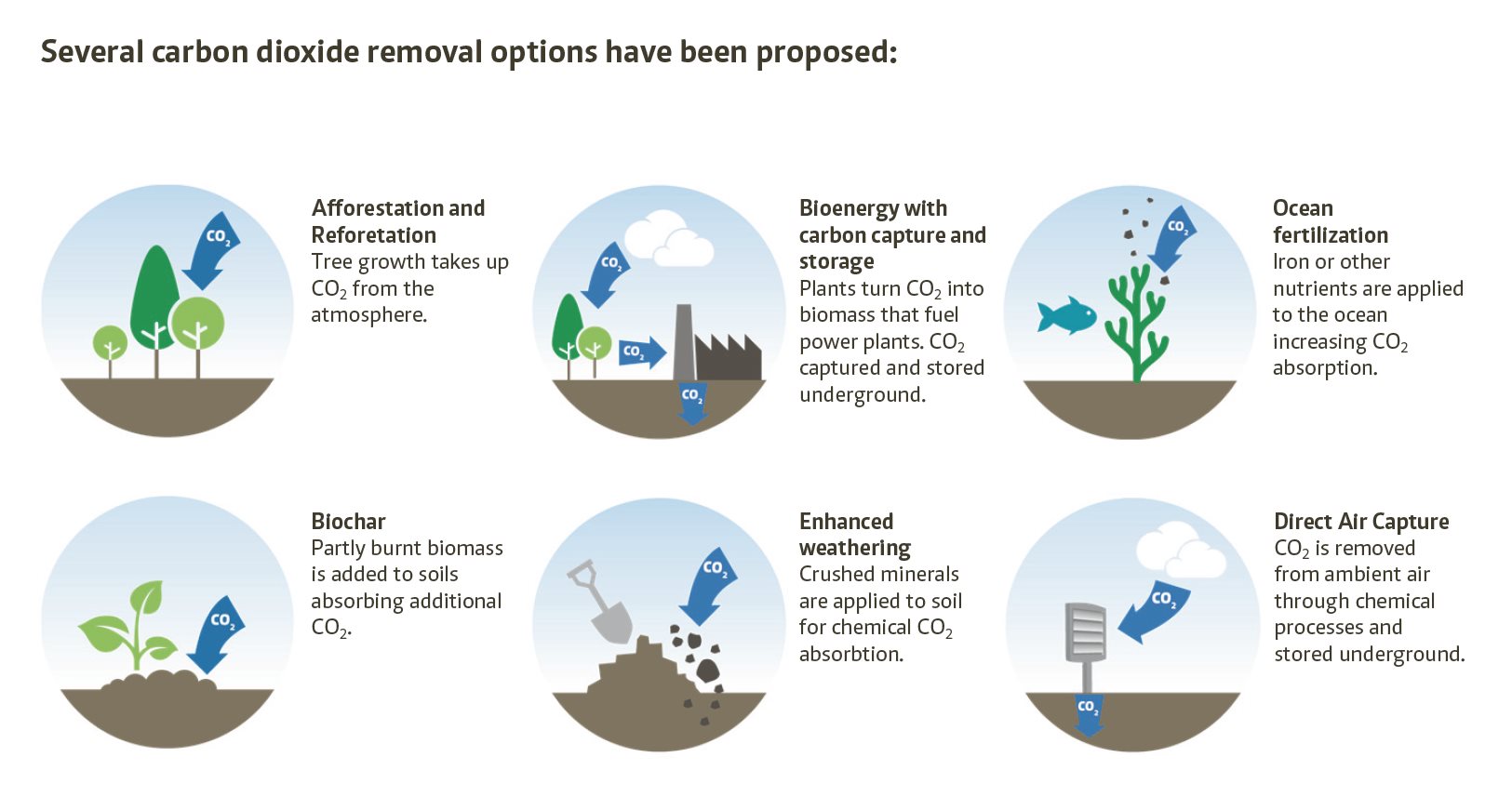
NETs aim to remove carbon dioxide (CO2), the major driver of man-made climate change, from the atmosphere. They include relatively simple options like planting more trees to lock up CO2 as they grow, or crushing rocks that naturally absorb CO2 and spreading them on soils so that they remove CO2 more rapidly. Another option includes using chemicals to sequester CO2 from the air (direct air capture). A further option involves burning plants for energy and capturing the CO2 that would otherwise be released, then storing it permanently deep below the ground. This is called bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS).
The three new studies represent the most comprehensive literature review to date. They were prepared by an international consortium of 20 researchers at six institutes. Overall, more than 6,000 documents were considered on seven groups of technologies: BECCS, afforestation and reforestation, direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS), enhanced weathering, ocean fertilization, biochar and carbon sequestration in soil. Through a systematic process and big data methods, 1000 studies were identified that provided relevant information on the potential, costs and side effects of the various technologies for CO2 removal.
According to the studies, all technologies have relevant potential – except ocean fertilization. However, they differ in terms of costs, side effects, development status and long-term storage potential: Afforestation, for example, could already be carried out at large scale today, but the CO2 could be released more easily again by human or natural influence. BECCS could safely store large quantities of CO2, but the technology is still in the demonstration phase and faces opposition from the public.
"If negative emissions technologies are to be massively scaled up by mid-century in the way many IAM scenarios portray them, then the innovation literature implies that we should be seeing demonstrations, niche applications, and early adoption occurring imminently," says co-author Greg Nemet of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, who led the review on NETs innovation and upscaling. "However, the NETs literature we reviewed does not at all reflect this urgency, nor do existing policies."
Through their systematic literature analysis, the researchers have found that almost two-thirds of the literature focuses on the early phases of NET research and development. "The actual use of new technologies and their upscaling takes a lot of time. That makes it all the more important to support these steps through research," says Sabine Fuss, Head of the MCC working group Sustainable Resource Management and Global Change. "In order to clarify the opportunities and risks of negative emissions and to make them possible on an industrial scale, a roadmap for pilot projects must be developed. This will certainly have to cover several different technologies – a focus on just one technology at this scale would be too risky".
More information:
Minx, Jan C. et al. (2018): Negative emissions: Part 1—research landscape and synthesis. Environmental Research Letters 13, 063001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aabf9b
Fuss, Sabine et al. (2018): Negative emissions—Part 2: Costs, potentials and side effects. Environmental Research Letters 13, 063002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aabf9f
Nemet, Gregory F. et al. (2018): Negative emissions—Part 3: Innovation and upscaling. Environmental Research Letters 13, 063003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aabff4
This press release was published by Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC).


